Multilevel Modeling
aML
Likelihood and Predictions of Multinomial Probit Model
This note describes how to calculate the likelihood of a multinomial probit. By trivial extension, it permits calculating the predicted probabilities of an estimated multinomial probit model.Consider a binomial probit with potential outcomes Y∈{0,1,2}. The discussion below readily generalizes to higher-order multinomial probits. Associated with each outcome is a so-called value function. We arbitrarily select Y=0 as the omitted category, i.e., with zero value function:
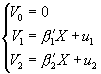
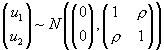 . The outcome corresponds to whichever value function is
greatest:
. The outcome corresponds to whichever value function is
greatest:
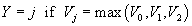 .
.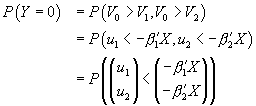
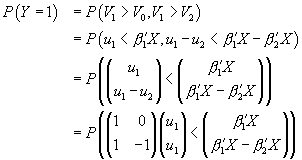
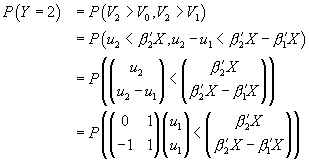
All three probabilities involve a cumulative bivariate normal
probability. The first is trivial: 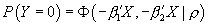 .
For the others, we first need to determine the bivariate covariance matrices.
The covariance matrix for
.
For the others, we first need to determine the bivariate covariance matrices.
The covariance matrix for 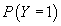 is
is 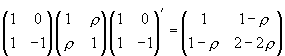 and thus
and thus
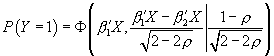 . The last covariance matrix is
. The last covariance matrix is
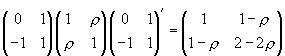 and thus
and thus 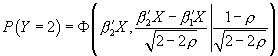 .
.
Internally, aML Version 2.0 follows a generalized version of the above discussion: it converts every n-nomial probit outcome into n correlated probit outcomes.
The likelihood and predicted probabilities may readily be estimated using any
statistical package that supports the bivariate cumulative normal probability
function. We illustrate the implementation in Stata with ado file
binphat.ado
(binomial probit hat). It takes 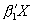 ,
,
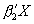 , and ρ as inputs and generates three probability variables
corresponding to
, and ρ as inputs and generates three probability variables
corresponding to 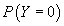 ,
, 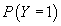 ,
and
,
and 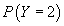 .
.
Back to Frequently Asked Questions
Back to technical support
Back to home